Introduction
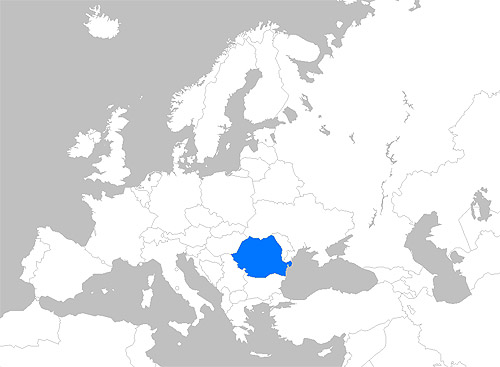 Romania is a country located at the intersection of Central and Southeastern Europe, bordering on the Black Sea. Romania shares a border with Hungary and Serbia to the west, Ukraine and Moldova to the northeast and east, and Bulgaria to the south. At 238,400 square kilometers (92,000 sq mi), Romania is the ninth largest country of the European Union by area, and has the seventh largest population of the European Union with more than 19 million people.
Romania is a country located at the intersection of Central and Southeastern Europe, bordering on the Black Sea. Romania shares a border with Hungary and Serbia to the west, Ukraine and Moldova to the northeast and east, and Bulgaria to the south. At 238,400 square kilometers (92,000 sq mi), Romania is the ninth largest country of the European Union by area, and has the seventh largest population of the European Union with more than 19 million people.
Its capital and largest city is Bucharest, the ninth largest city in the EU.
With the fall of the Iron Curtain and the 1989 Revolution, Romania began its transition towards democracy and a capitalist market economy. After a decade of post-revolution economic problems and living-standards decline, extensive reforms fostered economic recovery. As of 2010, Romania is an upper-middle-income country with a high human development index.
Romania joined NATO on 29 March 2004, and the European Union on 1 January 2007. It is also a member of the: Latin Union, Francophonie, OSCE, WTO, BSEC, United Nations, etc. Today, Romania is a unitary semi-presidential republic, in which the executive branch consists of the President and the Government.
With a GDP of around $267 billion and a GDP per capita (PPP) of $12,476 for the year 2011, Romania is an upper-middle income country economy and has been part of the European Union since 1 January 2007.
Since the country’s accession to the European Union, this has begun to change. After being slashed by 50% in 2009 due to the global recession, R&D spending was increased by 44% in 2010 and now stands at $0.5 billion (1.5 billion lei). The country has joined or is about to join several major international organizations such as CERN and the European Space Agency. Overall, the situation has been characterized as “rapidly improving”, albeit from a low base.
Science and technology
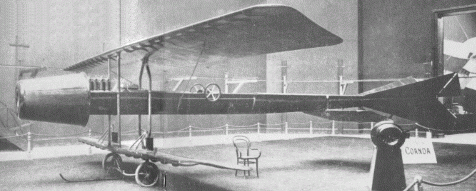 Historically, Romanian researchers and inventors have made notable contributions to several fields, such as: aeronautics, medicine, mathematics, computer science/engineering, physics, biophysics, chemistry, biochemistry and biology. In the history of flight, Traian Vuia made the first airplane to take off on its own power and Aurel Vlaicu built and flew some of the earliest successful aircraft. Also, Henri Coandă discovered the Coandă effect of fluidics. Preceding him, Elie Carafoli was a pioneering contributor to the field of aerodynamics in the world.
Historically, Romanian researchers and inventors have made notable contributions to several fields, such as: aeronautics, medicine, mathematics, computer science/engineering, physics, biophysics, chemistry, biochemistry and biology. In the history of flight, Traian Vuia made the first airplane to take off on its own power and Aurel Vlaicu built and flew some of the earliest successful aircraft. Also, Henri Coandă discovered the Coandă effect of fluidics. Preceding him, Elie Carafoli was a pioneering contributor to the field of aerodynamics in the world.
Victor Babes discovered more than 50 germs and a cure for a disease named after him, babesiosis; biologist Nicolae Paulescu discovered insulin. Another biologist, Emil Palade, received the Nobel Prize for his contributions to cell biology. George Constantinescu created the theory of sonics, while Lazăr Edeleanu was the first chemist to synthesize amphetamine and also invented the modern method of refining crude oil. Costin Nenițescu found new methods for the synthesis of pirilium salts, of carbenes, tryptamine, serotonin, two new syntheses for the indole nucleus, and a new method of polymerisation of ethylene.
Several mathematicians distinguished themselves as well, among them: Gheorghe Titeica, Spiru Haret, Grigore Moisil, Miron Nicolescu, Nicolae Popescu and Stefan Odobleja; the latter is also regarded as the ideological father behind cybernetics.
The Romanian mathematics team is the first in Europe and 10th in the world, a performance recently acquired.

Notable physicists and inventors also include: Horia Hulubei in atomic physics, Serban Titeica in theoretical physics, Mihai Gavrila specialized in quantum theory and discoverer of the atomic dichotomy phenomenon, Al
The nuclear physics facility of the European Union’s proposed Extreme Light Infrastructure (ELI) laser will be built in Romania. Romania currently has 1,400 MW of nuclear power capacity by means of one active nuclear power plant (Cernavodă) with 2 reactors, which constitutes around 18% of the national power generation capacity of the country. This makes Romania the 23rd largest user of nuclear power in the world. Alexandru Proca (known for the first meson theory of nuclear forces and Proca’s equations of the vectorial mesonic field), Stefan Procopiu known for the first theory of the magnetic moment of the electron in 1911 (now known as the Bohr-Procopiu magneton), Theodor V. Ionescu, the inventor of a multiple-cavity magnetron (1935), a hydrogen maser in 1947, 3D imaging for cinema/television in 1924 and hot deuterium plasma studies for controlled nuclear fusion, Ionel Solomon known for the nuclear magnetic resonance theory in solids, Solomon equations and photovoltaic devices, Petrache Poenaru, Nicolae Teclu and Victor Toma, with the latter known for the invention and construction of the first Romanian computer, the CIFA-1 in 1955.
In early 2012, Romania launched its first satellite from the Centre Spatial Guyanais in French Guyana.
Information technology
Romania is one of the fastest-growing information technology (IT) markets in Central and Eastern Europe. The country has made significant progress in all of the information and communications technology (ICT) subsectors, including basic telephony, mobile telephony, the Internet and IT. The country’s telecoms sector has been deregulated, expanded and modernised over the past 15 years.
Romania is the leader in Europe, and sixth in the world, in terms of the number of certified IT specialists, with density rates per 1,000 inhabitants greater than in the US or Russia. There are almost 100,000 specialists in the IT sector. Approximately 5,000 of the 30,000 engineers graduating every year in Romania are trained in ICT.
Microsoft acquired Romanian Antivirus Technology in 2003. According to Microsoft, Romania has a clear potential in information technology, an area in which Romanian students, researchers and entrepreneurs excel. Its western-oriented culture and the high educational degree of its youth bring Romania forward as a huge potential market (the second largest software producer in Eastern Europe). In terms of IT outsourcing services Romania is ranked in the third place worldwide successfully challenging India.
 The IT market is one of the most dynamic sectors of the Romanian economy. Since the year 1994 the IT market has demonstrated growth rates of 40–60 percent a year. The biggest sector in terms of revenue is system and network integration, which accounts for 28,3% of the total market revenues. Meanwhile the fastest growing segment of the IT market is offshore programming. The industry of software development outsourcing crossed the mark of $3 billion of total revenues in 2005 and reached $4.8 billion in 2006. Nowadays it account for about 6-10% from the GDP.
The IT market is one of the most dynamic sectors of the Romanian economy. Since the year 1994 the IT market has demonstrated growth rates of 40–60 percent a year. The biggest sector in terms of revenue is system and network integration, which accounts for 28,3% of the total market revenues. Meanwhile the fastest growing segment of the IT market is offshore programming. The industry of software development outsourcing crossed the mark of $3 billion of total revenues in 2005 and reached $4.8 billion in 2006. Nowadays it account for about 6-10% from the GDP.
Currently Romania controls 5 percent of the offshore software development market and is the third leading country (after India and China) among software exporters. Such growth of software outsourcing in Romania is caused by a number of factors. One of them is the supporting role of the Romanian Government. The Government has launched a program promoting construction of IT-oriented technology parks – special zones that have an established infrastructure and enjoy a favorable tax and customs regime. Another factor stimulating the IT sector growth in Romania is the presence of global technology corporations such as Intel, Motorola, Sun Microsystems, Boeing, Nokia and others, which have intensified their software development activities and opened their R&D centers in Romania.
The ICT industry has broadened its focus beyond manufacturing equipment to maintenance and management services as well as creating audio, video, print and digital content. These developments are anticipated to create a variety of new opportunities in Romania’s ICT market. On the occasion of the World Electronics Forum (Paris 2000), the “Worldwide ICT Professionals Market Situation Study” showed that, by 2008, Romania will be the only European country to have excellent IT specialists.
Romania’s main competitive advantage in software development consists of its highly qualified, cost-effective human resources.
Currently, about 25,000 software professionals work in the industry and almost 1/5 of them are involved in software export activities. Romania ranks the 6th in the world by number of certified professionals (“2003 Global Skills IQ Report”, Brainbench) and has been awarded a bronze certificate in the category of “Most Certified Nation (Overall)” during the first annual Bench Games 2005 (“2005 Bench Games Report”, Brainbench). Vicepresident for EMEA, showed that Oracle is committed to encourage this country to take advantage of its potential: “Oracle aims to help push Romania into becoming the Silicon Valley of Central and Eastern Europe.”
In Romania there are 7.8 million connections to the Internet, out of which 4 million are broadband (end of 2010).
Country code (Top level domain): .ro
There were approximatively 250 000 domains registered under .ro at the end of 2007. This number had risen to over 340,000 in November 2008 and in 2012 the number went even higher: over 600,000 (710,000 domains in 2013).
 Based on Akamai report at January 2011, Constanţa, Iasi and Timisoara are in the top 100 cities at the world level with the highest average Internet speeds.
Based on Akamai report at January 2011, Constanţa, Iasi and Timisoara are in the top 100 cities at the world level with the highest average Internet speeds.
Based on Pando networks content delivery service released on September 2011, Romania is in the top 5 Internet speeds in the world (2013) averaging at 37 Mbit/s download. Romania surpassed Bulgaria, Lithuania and Latvia on the top five, while the United States was only the 14th.
For business use, services are usually provided through fiber optics or radio. Companies providing such services are providing very flexible and negotiable plans also based on the Metropolitan/International distinction. Usually prices and bandwidths are fully negotiable, with the micro-ISPs discussed above being influential resellers. There is very strong competition, with no peering between many such companies (again requiring a lot of traffic to be routed through international routes) and not even access to another’s fiber-optics infrastructure (leading to the existence, in some cases, of over 25 fiber optics cables on the same street, hanging from the same pole). As such many companies have two separate providers for basically the same services.
Romania is aggressively promoting and developing its biotechnology industry. Hundred of millions of dollars were invested into the sector to build up infrastructure, fund research and development and to recruit top international scientists to Romania. Romania features one of the world’s newest competitive bio-industries, in key areas as pharmacogenomics, protein engineering, glyco-engineering, tissue engineering, bio-informatics, genome medicine and preventive medicine. Romania is devoting substantial resources to developing universities and R&D facilities, increasing bioventure startups, growing bio-clusters (communities of biotechnology companies and institutions) and developing human resources, all with the goal of making it one of the world’s most advanced biotechnology regions.
More:
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Romania
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Industry_of_Romania
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_in_Romania
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Science_and_technology_in_Romania
- http://www.businessinsider.com/europe-fastest-connections-2011-11?op=1
- http://www.rotld.ro
- http://rost.ancs.ro
- http://www.aries.ro
- http://www.anis.ro
- http://www.apti.ro
- http://www.nytimes.com/2011/10/31/business/global/31iht-RCE-ROMANIA31.html?pagewanted=all
- http://techcrunch.com/2012/05/05/with-a-talent-war-in-the-valley-perhaps-romania-has-the-answers
- http://www.forbes.com/sites/alisoncoleman/2014/03/27/europes-hidden-entrepreneurial-tech-hotbed-romania-powers-up/
